Provenance Tagging and Trust: How to Build AI-Friendly Authority
The internet has a trust problem.
In a world of synthetic content, deepfakes, and AI-generated misinformation, credibility is no longer something you earn once — it’s something you maintain through proof.
As MIT Technology Review put it, we’re entering an era where content must come with receipts. And that’s where provenance tagging comes in.
The Trust Crisis in the Age of AI
AI has changed how content is created, shared, and verified. According to Forbes, misinformation and AI hallucinations have eroded consumer confidence in digital content by nearly 40% in just two years. Nieman Lab reports that trust in online news is at a record low, while Reuters emphasizes the importance of transparency and verifiable authorship in digital journalism.
When generative engines like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity summarize the web, they don’t just retrieve content — they reinterpret it. That makes it critical that your brand’s information not only exists online but carries verifiable proof of authorship and authenticity.
This is where provenance tagging becomes a bridge between credibility and visibility.
What Is Provenance Tagging — and Why It Matters
Provenance tagging is the practice of embedding verifiable metadata into digital content to confirm who created it, when, and how it has been modified. Think of it as a digital fingerprint for your ideas.
Organizations like Adobe (through the Content Authenticity Initiative) and the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) are leading the charge to create open standards that allow audiences — and machines — to see exactly where content comes from.
For businesses optimizing for GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) and LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization), provenance tagging is more than a transparency tool. It’s a trust signal for both humans and AI systems.
Generative engines are increasingly prioritizing content that demonstrates factual integrity and verified authorship. As Google DeepMind explains, provenance will play a vital role in determining which information large language models trust, cite, and reuse.
Provenance tagging is how you say, "Yes, this is ours — and here’s the proof."
How AI Uses Provenance to Decide What to Cite
When an AI system retrieves data, it looks for more than keywords. It looks for context, authority, and attribution. Provenance metadata gives LLMs the signals they need to understand whether your content is original, trustworthy, and safe to reference.
According to OpenAI and BBC R&D, provenance tags serve as a credibility layer that helps models trace where an idea originated. They ensure that when your work is cited, it’s properly attributed.
That attribution isn’t just ethical; it’s strategic. Verified authorship improves your visibility inside generative answers — an emerging form of what Search Engine Land calls “AI inclusion ranking.”
If your site doesn’t include structured author and source metadata, your content might never appear in AI-generated responses, even if it ranks well in Google.
To optimize both trust and retrievability, provenance tagging must be part of your GEO and LLMO strategy.
Related: The Future of Search: Why GEO Is the Next SEO
Step-by-Step: How to Implement Provenance Tagging
1. Start with Metadata Hygiene
Before advanced tagging, ensure your core metadata is clean and complete. This includes:
Author and organization name
Date created and modified
Copyright information
Content type (article, image, video, dataset)
Follow IPTC and EXIF metadata standards for visual and written content. As Reuters Trust Principles outline, consistent metadata is foundational to digital integrity.
Use tools like ExifTool or Adobe Bridge to inspect and edit metadata.
2. Adopt Open Standards: C2PA & CAI
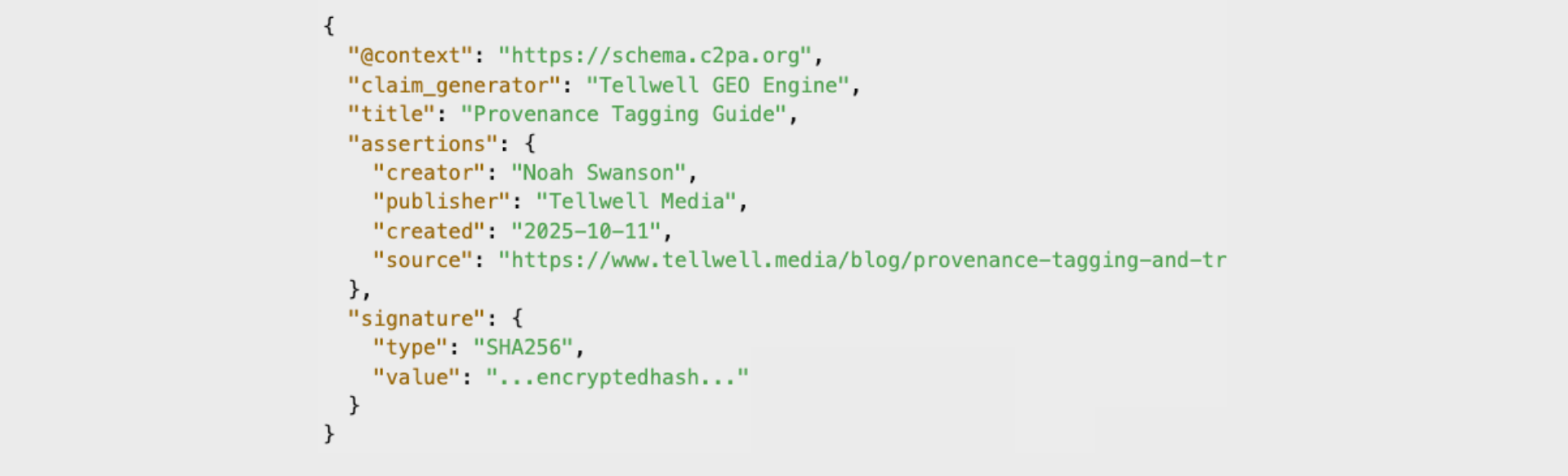
The C2PA (Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity) provides a framework for embedding cryptographically signed manifests into content. These manifests store details such as creator, edit history, and verification hashes.
Example JSON structure for a simple C2PA manifest:
This ensures that your content’s origin can be verified through a secure chain of trust.
Learn more from Adobe’s Content Authenticity Initiative and Numbers Protocol, which both advocate for transparent, interoperable provenance systems.
3. Add Schema Markup (JSON-LD) for Ownership Transparency
Structured data markup communicates ownership, publication, and modification data to search engines and AI models.
Below is an example of extended BlogPosting schema incorporating provenance details:
You can test this with Google’s Rich Results Tool or similar schema validators.
More examples: Snippet Engineering & RAG Testing
4. Monitor Provenance Integrity
Verification doesn’t stop after publishing. Provenance can degrade when content is copied, scraped, or modified.
To maintain trust signals:
Use contentauthenticity.org and TruLens AI for authenticity validation.
Periodically verify C2PA signatures and timestamps.
Register digital assets in blockchain-based systems like Numbers Protocol for immutable provenance tracking.
These steps help maintain credibility even as content is syndicated or quoted elsewhere.
How Provenance Strengthens GEO and LLMO
According to a16z, provenance isn’t just a technical standard; it’s an optimization layer for the AI web. Generative engines favor content that can prove its authorship and authenticity through structured signals.
When provenance data aligns with GEO structure (clear hierarchy, canonical definitions, linked schema), AI systems can:
Verify factual grounding before retrieval.
Attribute ideas correctly in generated responses.
Rank content higher for authority and reliability.
This is what Search Engine Land calls the new trust stack — where visibility is earned through verifiability.
That makes provenance tagging one of the most important technical steps for modern SEO and GEO strategy.
Related: Embedding Optimization: How AI Reads and Retrieves Your Content
Case Studies and Emerging Best Practices
BBC R&D uses C2PA manifests to ensure source transparency for AI training data.
Adobe Stock embeds CAI provenance in images to track derivative works.
Reuters employs blockchain verification for certain editorial assets.
Google DeepMind has proposed provenance-based ranking factors for AI-generated content.
OpenAI is collaborating with C2PA to integrate provenance data into RAG systems.
Each of these examples points to the same conclusion: trust is now a data layer.
In the GEO era, provenance is the connective tissue between your content and the AI systems that interpret it.
The Future of Provenance and AI Trust
As Stanford HAI and NYU’s Center for Responsible AI note, provenance will become a standard requirement for content indexing and model training datasets within the next few years.
Expect future content pipelines to include automated provenance APIs and compliance checks, where every article, video, or dataset must carry verifiable origin data before publication.
In that future, provenance isn’t optional. It’s infrastructure.
FAQ
-
Provenance tagging is the process of embedding verifiable metadata (like author, creation date, and modification history) into content to confirm its authenticity and origin. It acts as a digital fingerprint, allowing both humans and AI systems to verify who created a piece of content and how it has changed over time.
-
Provenance tagging strengthens both SEO and GEO by adding trust signals that AI models can interpret. When your content includes verifiable authorship and source data, generative engines like ChatGPT and Gemini are more likely to cite it in their responses — improving your authority and discoverability.
-
Start by cleaning your basic metadata (author, date, copyright info), then use standards like IPTC, EXIF, and C2PA manifests to embed verifiable data. You can also add provenance details directly into your BlogPosting schema using JSON-LD.
-
You can use tools such as Adobe’s Content Authenticity Initiative, Numbers Protocol, and TruLens AI to validate content authenticity and trace digital assets. These help ensure your provenance data remains intact even if content is shared or modified.
-
Generative AI systems prefer verifiable, trustworthy data. Provenance tagging gives your content machine-readable proof of authenticity — increasing the likelihood that your information is retrieved, cited, and reused by AI models.
Key Takeaway
Provenance tagging is more than metadata management — it’s brand reputation encoded in data.
When your content can prove its origin, it doesn’t just build human trust; it builds machine trust. And in the age of generative AI, that might be the most valuable kind there is.
References
MIT Technology Review — The Race to Watermark AI Content
Reuters Trust Principles
Google DeepMind: Building Trust in AI Systems
Stanford HAI — The Future of Authentic Media
Nieman Lab — How Journalists Use Provenance
TruLens AI Verification Tools
Forbes — Why Provenance Will Define the Next Era of Digital Trust

Author: Noah Swanson
Noah Swanson is the founder and Chief Content Officer of Tellwell.